What should the data structure be? ~How to use "vertical" and "horizontal" data structures.
Last Updated: 2025 / 03 / 07
Published: 2022 / 07 / 08
It has become a common practice in recent corporate activities to manage data in databases and utilize the results of analysis for business purposes through BI tools and other tools. Data is often managed in a tabular format consisting of rows and columns, and there are two main design methods: "vertical" and "horizontal. Many people may not know how to distinguish between these two design methods. In this issue, we will explain how to distinguish the use of vertical and horizontal data.
Horizontal data is a data structure in which different items are placed in rows and columns, and information is represented by the correspondence between the rows and columns.
For example, in the following example of sales data of a supermarket, the rows contain items to be aggregated such as "sales," "gross profit," and "gross profit margin," and the columns contain items indicating the year and the month. Corresponding to these items, data is stored in the form of "Sales" in the second row × "January 2022" in the second column = "Sales in January 2022.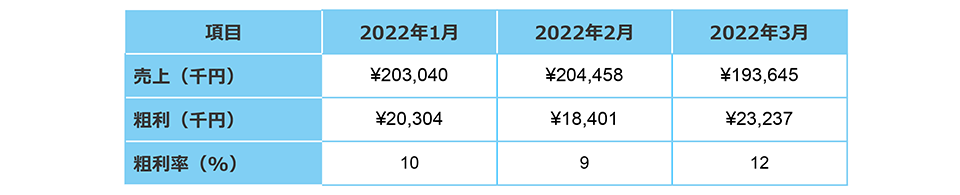
The following is an example of a company's quarterly sales of office supplies, shown horizontally. In this example, the rows contain the period items and the columns contain the product category items, and the matrix is switched from the previous example.
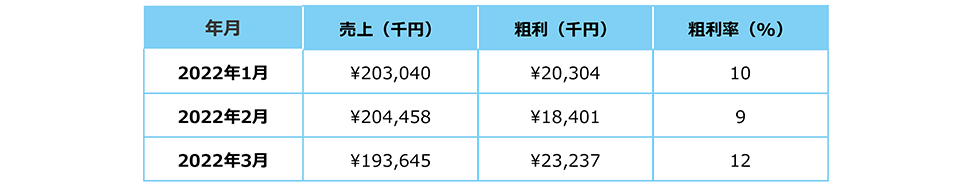
Vertical data, on the other hand, is in a format in which corresponding data is added vertically to items arranged in columns. For example, in the example of the supermarket sales data shown in the previous section, items such as "year, month," "sales," "gross profit," and "gross profit margin" are arranged in columns, and the information corresponding to each column is stored from the second row.
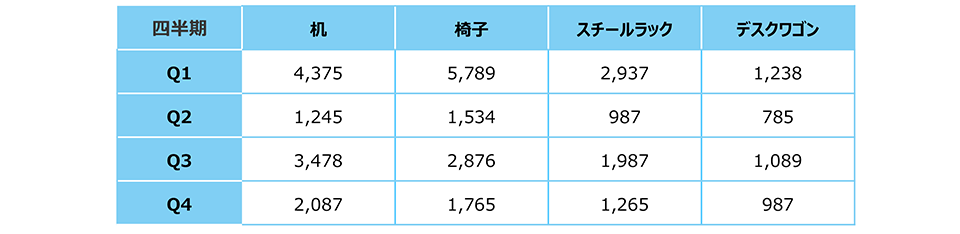
Also, the quarterly sales numbers for office supplies for the same company mentioned earlier are shown below in a vertical holding format. Here, too, items such as "Product," "Quarter," and "Sales Quantity" are arranged in columns, and the corresponding information is stored in the second and subsequent rows.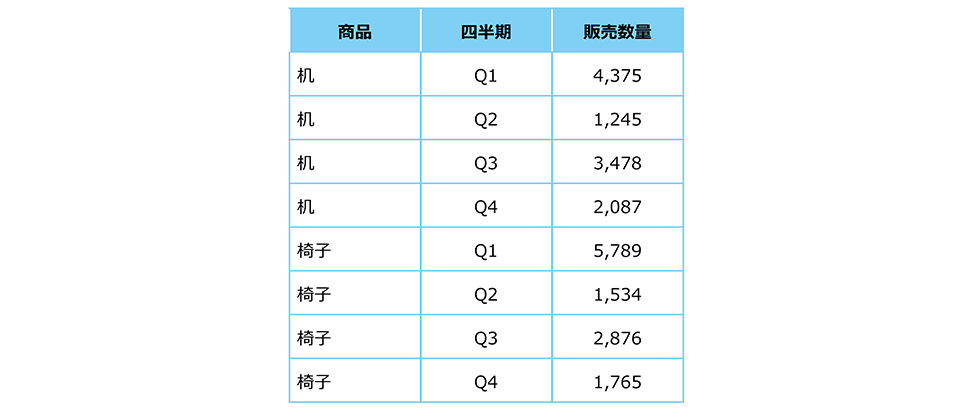
An item-by-item comparison of the characteristics of the vertical and horizontal holding formats is shown below.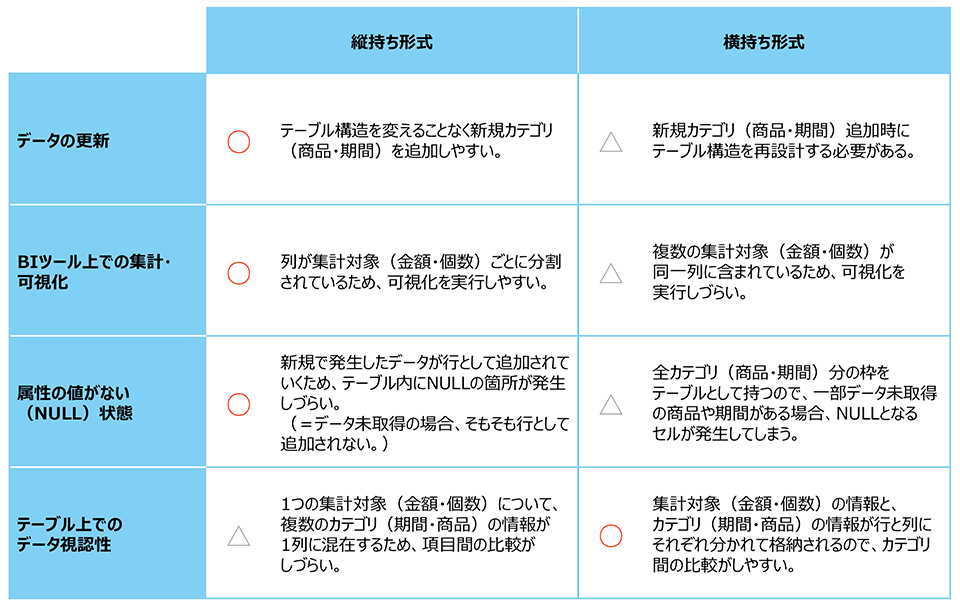
As can be seen from the above comparison, when handling data for management and aggregation in a database or BI tool, the basic "vertical" format is more suitable for easy updating and aggregation. On the other hand, when data is output for comparison by product or time period axis, "horizontal data" is recommended due to its superior visibility.
It is advisable to decide which structure to use for storing and managing data after imagining the situations in which the data will be handled.
RDB is an abbreviation for Relational Database, which translates to relational database. It is a database management method that manages data as multiple tables and defines the relationship between tables to handle complex data relationships. RDB is generally used in the database software used for business purposes these days.
Vertical data is also more suitable for constructing such RDBs.
For example, when managing school grades, the attributes are "student number," "name," "grade," "English," "math," "science," "social studies," etc. In the case of horizontal data, if you want to add new scores for "physical education," you need to change the table design. In contrast, vertical tables can be managed more smoothly, since it is simple to insert "student number, name, PE, and PE score.
In addition, the most common use of RDB is to specify conditions and search only for data matching those conditions. In the horizontal mode, it is necessary to specify multiple column names to specify conditions, but in the vertical mode, it is easy to search by specifying a condition for a single column name.
We have looked at the difference between "vertical" and "horizontal" formats, and we hope you have understood that the vertical format is more suitable for management and tabulation on a database or BI tool.
The issue that tends to become a challenge when taking this into consideration is the conversion of survey data into databases and BI tools. As shown below, general survey data is in a horizontal format, with respondent sample numbers in the rows and answered question numbers in the columns, and response values are stored in a matrix correspondence. As explained so far, it is rather difficult to handle this data format in a database or B-tool, and it is desirable to convert it to a vertical format.
Cross Marketing converts such survey data into a vertical format, and provides a full range of services, including the creation of BI dashboards that are ideal for tabulation and visualization.We can also handle data from surveys other than those conducted by our company, so please feel free to contact us if you have any questions about converting survey data into a database or implementing BI.
■Reference site:
https://newssdx.kcme.jp/tableau_beginner_data_vertical_horizon/
https://mathwords.net/yokomotitatemoti
https://qol-kk.com/wp2/blog/2021/08/02/post-2981/
http://navi.wingarc.com/drsum/post-97.html
https://manamina.valuesccg.com/articles/740
https://octopus.nehan.io/manual/3340
https://zenn.dev/mkz/articles/7420f168c35550
